

Предисловие
Карповые (Cyprinidae) - самое представительное семейство современных рыб (275 родов и около 1800 видов). Только в реках и озерах на территории СССР обитает 58 родов видов.
Морфологические признаки, общие для карповых: тело покрыто циклоидной чешуей, реже голое; на нижней стороне черепа роговидное образование (жерновок), служащее для перетирания пищи; немногочисленные одно-трехрядные глоточные зубы; усиков нет или не более двух пар (исключение - восьмиусый амурский пескарь).
Местом возникновения карповых был тропический Афро-Азиатский регион (древнейшие рода - барилии и троегубы). Сегодня они населяют пресные и солоноватые (5 - 14 ‰) воды всех частей света, кроме Австралии, Южной Америки и о. Мадагаскара. Только дальневосточные красноперки живут при океанической солености - 35‰, а слепые Caecobarbus geertsi, Caecocypris basimi и Typhlogarra widdowsoni обосновались в подземных водоемах. Карповые питаются фито- и зоопланктоном, бентосными организмами, но есть среди них хищники (Aspiolucius, Culler, Luciosoma и др.), любители детрита и перифитона (Discolabeo, Mekongina, Morulius и т. п.), водной растительности (Scardinus, Ctenopharyn-godon и пр.).
Представители родов Epalzeorhynchus, Garra выполняют функции санитаров, очищая покровы рыб от паразитов.
Выведение причудливых форм и окрасок золотых рыбок, а также разноцветных карпов (кои) - многовековая традиция в Китае и Японии.
Половой зрелости эти рыбы, как правило, достигают в 6 - 18 месяцев. Производителей подбирают из стаи мальков. Самцы обычно мельче, стройнее, ярче окрашены (иногда на голове, плавниках и верхней части туловища есть роговидные бугорки). За две-три недели до нереста производителей разделяют и кормят разнообразной пищей. Толчком к нересту служат: свежая мягкая вода, повышение температуры на 3 - 5° С. наличие необходимого субстрата, высокая проточность воды, световая обработка в ночное время (имитация лунных фаз).
Для разведения используют низкие (15 - 50 см), лучше бескаркасные аквариумы с большой площадью дна, где желательно поместить нерестовые решетки. Нерест стайный, реже парный. Икра приклеивается к растениям или плавает в толще воды. У Hyhorhynchus, Notropis, Pimephales, Rhinichthys, Campostoma и др. кладку охраняет самец, а самки Chilogobio. Tanakia и др. прячут икру в мантийную полость моллюска и различные донные щели. Продуктивность варьирует oт 50 до 50 тысяч и более шгук.
Для дезинфекции икры воду озонируют или добавляют в нее метиленовую синь, окситетрациклин (5 - 10 мг/л) и т. п. Стандартный инкубационный период 18 - 36 часов еще через 3 - 5 дней молодь начинает плавать и питаться "живой пылью".
Стайный образ жизни, дружелюбность, пестрый наряд делают карповых желанными гостями в аквариумах.
А. Кочетов
Cyprinids (Cyprinidae) are the most impressive family of contemporary fishes (it includes 275 genera and approximately 1,800 species). On the territory of the USSR only 58 genera and 126 species inhabit rivers and lakes.
Morphologic characteristics common to all Cyprinids are the following: the body is covered with cycloid scales, seldom naked; on the lower side of the skull is a spiny protuberance which serves to crush the food; a few pharyngeal teeth are disposed in one to three rows; barbels are absent, or there are no more than two pairs (with the exception of the Amur Eight-Barbel Gudgeon - Gobiobotia pappenheimi).
Cyprinids originate in the tropical regions of Africa and Asia (most archaic genera are Rajamas (Barilius) and Three-Lips (Opsariichthys). Today they inhabit fresh and salty (5-14 ‰) waters in all parts of the world, except Australia, South America and Madagascar. Only the Far-Eastern Pacific Redfins (Tribolodon sp.) are capable of living in oceanic salinity of 35%, but the blind Caecobarbus geertsi, Caecocypris basimi and Typhlogarra widdowsoni have settled down in underground waters.
Cyprinids feed on phyto- and zooplankton and benthos, but there are among them carnivores (Aspiolucius, Culler, Luciosoma, etc.), detritus and periphyton lovers (Discolabeo, Mekongina, Morulius, etc.), as well as those thriving on water vegetation (Scardinus. Ctenopharyngodon, etc.).
Specimens of Epalzeorhynchus and Garra genera clear fishes' covers of parasites. In China and Japan there is a centuries-old tradition to breed odd forms and colour varieties of Goldfishes as well as multi-coloured Carps (Koi).
As a rule, Cyprinids reach sexual maturity at the age of 6 to 18 months. Spawners are selected among a shoal of fry. Males are usually smaller, slimmer and brighter than females (sometimes there are horny tubercles on the head, fins and upper side of the body of males). Two to three weeks before expected spawning, adult fishes are to be separated and fed with varied food. The following stimuli may provoke the spawning: fresh, soft water, rise in temperature by 3 to 5° C; necessary substratum availability, high water flowage, lighting at night (imitation of moon phases).
For breeding it is desirable to use tanks made wholly of glass with low depth (15 to 50 cm) and a large surface area furnished with spawning grids. Cyprinids spawn communally, seldom in single pairs. The eggs stick to water plants or float in open water. Males of Hyborhynchus, Notropis, Pimephales, Rhinichthys and Campostoma protect the clutch, while females of Chilogobio, Tanakia and other genera hide the eggs in the mantle cavity of mollusca and bottom cracks. Fecundity varies from 50 to 50,000 eggs and more. To disinfect the eggs one may ionize the water or add methylene-blue, oxytetracyclinum (5 to 10 mg/l) and so on. Standard incubation period is 18 to 36 hours; three to five days later the young begin feeding and swimming.
Communal mode of life, friendliness and their multi-coloured dress make Cyprinids popular with aquarium keepers.
Los ciprinidos (Cyprinidae) constituyen la familia de peces mas numerosa de nuestros dias (275 generos de 1.800 especies). Tan solo en aguas dulces del territorio de la URSS habitan 58 generos de 126 especies. Las caracterfsticas morfologicas comunes de los ciprinidos: el cuerpo recubierto de escamas cicloideas; en algunas especies, desnudo. Una excrecencia cornea en la parte inferior del craneo que sirve de "muelilla" para triturar el pasto; dientes farfngeos formando de una a tres filas; falta de barbillas о presencia de dos pares de estas tan solo (salvo la excepcion de Gobiobotia pappenheimi, de ocho barbillas). Por su lugar de origen se tiene la region afroasiatica. Los generos mas antiguos: Barilius у Opsariichthys. Actualmente la familia se presenta en aguas dulces о росо salobres (5-14 ‰) de casi el mundo entero, menos Australia, America del Sur у Madagascar. Solo la especie Tribolodon, del Extremo Oriente, habita aguas de salobridad oceanica (35 ‰). у las especies ciegas de Caecobarbus geertsi, Caecocypris basimi у Typhlogarra widdowsoni se adaptaron a las aguas de estanques subterraneos.
Los ciprinidos se alimentan de fito- у zooplancton, organismos del bentos, pero tambien hay entre ellos peces carniceros (Aspiolucius, Culter, Luciosoma, etc.). hay amantes de detritus у periphyton (Discolabeo, Nekongina. Morulius, etc.), como tambien los hay fitofagos (Scardinus, Ctenopharyngodon у otros).
Los Epalzeorhynchus у Garra (algunas de las especies de estos generos) desemplean el papel de aseadores alimentandose de parasitos exteriores de otros peces.
La seleccion de las carpas doradas de formas у tintes rebuscados, como tambien la de carpas de colores variados (koi) es una tradicion de muchos siglos en China у Japon.
Estos peces pubescen generalmente a los 6-18 meses de vida. A los procreadores se ha de escojerlos de entre la cria joven. Por Io general, los machos suelen cederles a las hembras en tamano siendo al mismo tiempo mas esbeltos у de colores mas vivos. En algunas especies, los machos tienen unas excrecencias corneas en la cabeza, parte superior del tronco у las aletas. Con dos о tres semanas de antelacion, se los separa a los procreadores del resto de los peces, asegurando alimento intenso у variado. Los factores que estimulan la muga son el agua suave у renovada, la elevacion de la temperatura en 3 6 5° C, el substrato adecuado para la especie, un intenso flujo del agua у alumbramiento nocturno que imite las fases de la Luna.
Para las mugas se utilizan acuarios de reducida altura (15-50 cm.); son preferibles acuarios sin armazon alguna у con un vasto fondo. Se aconseja recurrir a unas rejillas especiales para obstaculizar a los peces el acceso a su propia puesta.
En los mas de los casos, se opera esta de manera gregal, habiendo casos. sin embargo, en que se celebra en parejas. Los huevos se pegan a las plantas о flotan en el espesor del agua. En las Hyborhynchus, Notropis. Pimephales, Rhinichthys, Campostoma у otras especies mas el macho cuida de la puesta. En las Chilogobio, Tanakia у otras especies afines la hembra logra insertar sus huevos en la cavidad paleal de los moluscos о albergarlos en rendijas que se presenten en el fondo. La productividad van'a entre 50 у 50 mil huevos у aun mas. Para la desinfeccion de la puesta se ozoniza el agua о se le adita el azul de metileno, oxitetraciclina (5-10 mg/l), etc. El pen'odo embrionario dura, por termino medio, de 18 a 36 horas. A los tres о cinco di'as de vida, los alevines empiezan ya a desplazarse en el agua у procurarse pasto.
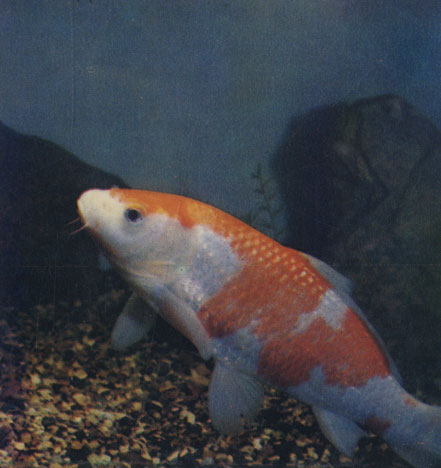

Краснопятнистый кои (Cyprinus carpio)

Эфиопский дискогнат (Garra sp. aethiopicus)

Верховка (Leucaspius delineatus)

Молодь оливкового барбуса (Barbus filamentosus)


